12 Sep 2022
12 Sep 2022
Africa is highly exposed to risks associated with climate change and biodiversity loss.
In 2022, the IPCC reported with ‘high confidence’ that the continent is already experiencing significant changes from climate change and that future impact on the region will be ‘substantial’.
Effects include ongoing and accelerating changes in rainfall patterns, water availability and heatwaves with a sharp reduction in agricultural productivity – the mainstay of many African economies – and increased climate-related ill-health and mortality.
The economic consequences are likely to be severe. According to calculations by the African Climate Policy Centre are likely to be as much as a 12% contraction of Africa’s gross domestic product (GDP).
Furthermore, biodiversity loss of forests and coastal ecosystems threaten the environment and livelihoods in Africa and will contribute to an acceleration in global climate change.
Despite these risks, finance for the maintenance and enhancement of Africa’s natural capital is grossly insufficient. There is a financing gap in Africa of more than $100 billion annually. The biggest gap is in the sustainable management of landscapes and seascapes – a key area for Africa given the lower carbon intensity of its economies relative to developed countries.
Moreover, the limited finance that is available is from public sources. But domestic public budgets do not have the potential to increase sufficiently to close the financing gap by 2030.
Without a step-change in finance, we will witness an accelerated decline in biodiversity, the collapse of ecosystems and repeated climate disasters leading to the reversal of decades of poverty reduction and economic growth in the region as well as the acceleration of the global climate crisis.
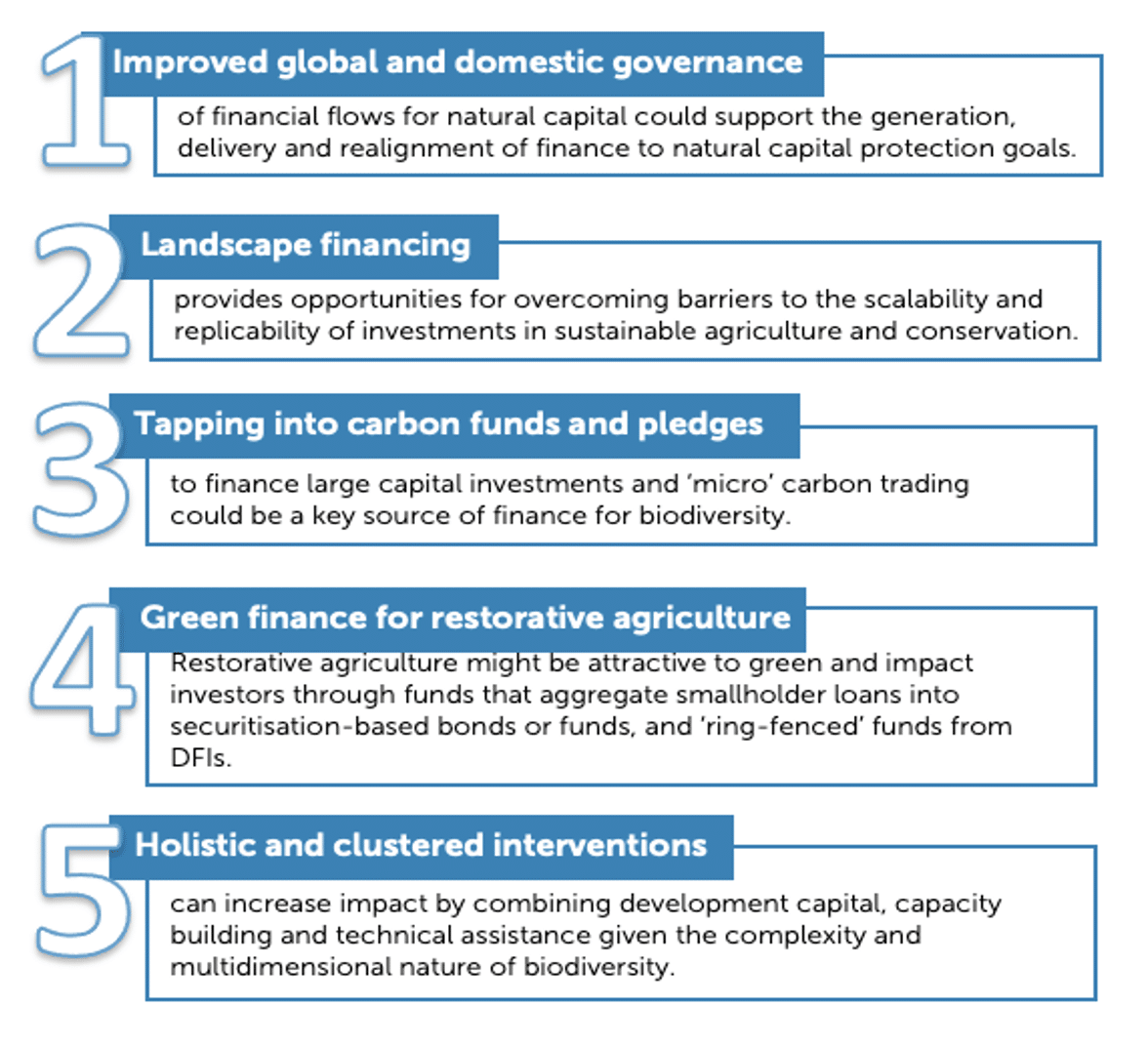
Given these challenges, this study, commissioned together with ODI, suggests five key approaches to greater mobilisation of finance for biodiversity in the region: