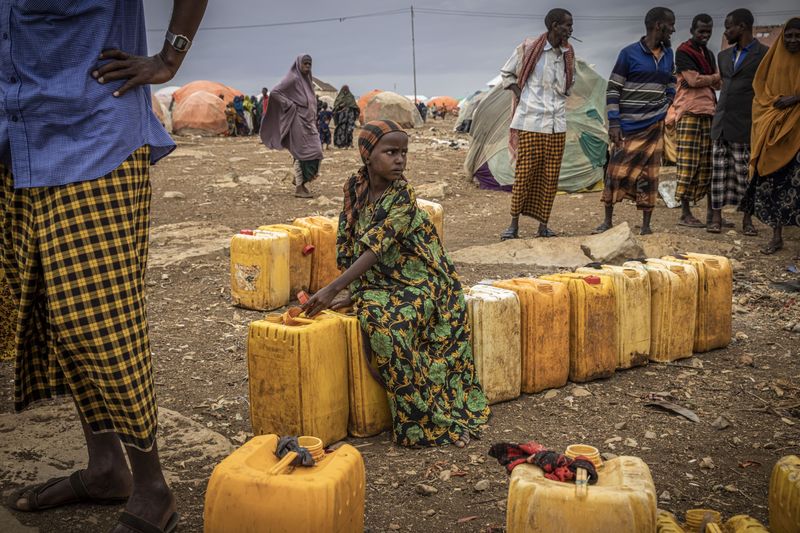
As the international climate community prepares to descend on Sharm el-Sheikh in Egypt, new analysis shows just how far off their host continent is in terms of attracting the finance it needs to adapt to catastrophic global warming, build renewable energy plants and enhance its carbon-absorbing ecosystems.
At $30 billion, annual climate finance flows in Africa are just 11% of the $277 billion needed, according to research published Wednesday by the Climate Policy Initiative, a US-based nonprofit. The research was commissioned by FSD Africa, an organization funded by the UK government, the Children’s Investment Fund Foundation, a charity set up by billionaire hedge fund activist Christopher Hohn, and UK Aid. It’s the first to map climate finance flows in Africa by region, sector and source, and captures available data for 2019 and 2020.
Top of the agenda at the November UN climate summit in Egypt, known as COP27, will be demands from developing nations for more funding from rich countries to adapt to global warming and a financing mechanism to help them cope with natural disasters and extreme weather events. In 2009, developed countries committed to $100 billion of assistance for poorer nations every year. They have fallen significantly short of that target.
Africa accounts for a tiny fraction of the world’s carbon emissions but its nations will be among the hardest hit by global warming, already manifested globally in disasters ranging from heat waves in Europe to droughts in the Horn of Africa and floods in Pakistan.
“A report such as this allows us to measure whether the commitments of developed countries to provide finance to developing countries, is indeed being delivered,” said Valli Moosa, deputy chairman and effective head of South Africa’s Presidential Climate Change Coordinating Commission, in a statement.
Private sector finance in particular remains too low, the Climate Policy Initiative said in the report. Companies and commercial financial institutions contributed just 14% of total climate finance received in Africa, much lower than in other developing regions.
What on Earth?What on Earth?What on Earth?The Bloomberg Green newsletter is your guide to the latest in climate news, zero-emission tech and green finance.The Bloomberg Green newsletter is your guide to the latest in climate news, zero-emission tech and green finance.The Bloomberg Green newsletter is your guide to the latest in climate news, zero-emission tech and green finance.
Existing flows are highly concentrated, with 10 of the 54 countries on the continent accounting for more than half of Africa’s climate finance. These include Egypt, Morocco, Nigeria, Kenya, Ethiopia and South Africa. The Southern African region bears the largest financing gap in absolute terms, attributed by the researchers to the $107 billion annual needs of South Africa alone, combined with one of the lowest regional levels of climate investment. As a percentage of gross domestic product, countries in Central and East Africa face the largest investment gaps.
Investment Opportunities
South Africa, the continent’s most industrialized nation, is transitioning from reliance on coal for more than 80% of its electricity to renewable energy, meaning that billions of dollars will need to be spent on new power plants and an expanded electricity grid.
“Public and private actors must act with scale and speed to help bring Africa’s climate goals to fruition,” said Barbara Buchner, global managing director of the Climate Policy Initiative. “Africa offers a wealth of climate-related investment opportunities” and “the social, economic, and environmental benefits which could be realized are even greater,” she said.
Those investment opportunities are spread across a number of sectors, including clean energy plants and agribusiness. Annual investment in renewable power stands at just 7% of the $133 billion that the International Energy Agency estimates African countries need to meet their 2030 energy and climate goals, according to the research. Agriculture and forestry investments are also falling short of financing needs.
Read original article