This month, we celebrate International Women’s Day united in the 2018 theme “Press for Progress.” While much of the discussion is around how global actors are pressing for progress on women’s equality at the macro level, I’d like to take a deeper look at how a low-income woman presses for progress in her own financial life.
Our program, Financial Sector Deepening Africa (FSD Africa), funded by UK aid from the UK government, is supporting Women’s World Banking’s partnership with Diamond Bank in Nigeria to improve access and usage of savings accounts among low-income clients, particularly women.
Three years into this partnership, we’re starting to understand just how transformational saving with a formal institution can be for women.
Women’s World Banking’s global research shows that women have specific and often complex savings needs. They are juggling scarce resources to cover day-to-day expenses with an eye toward the future. They save against emergencies and toward goals such as education and business growth.
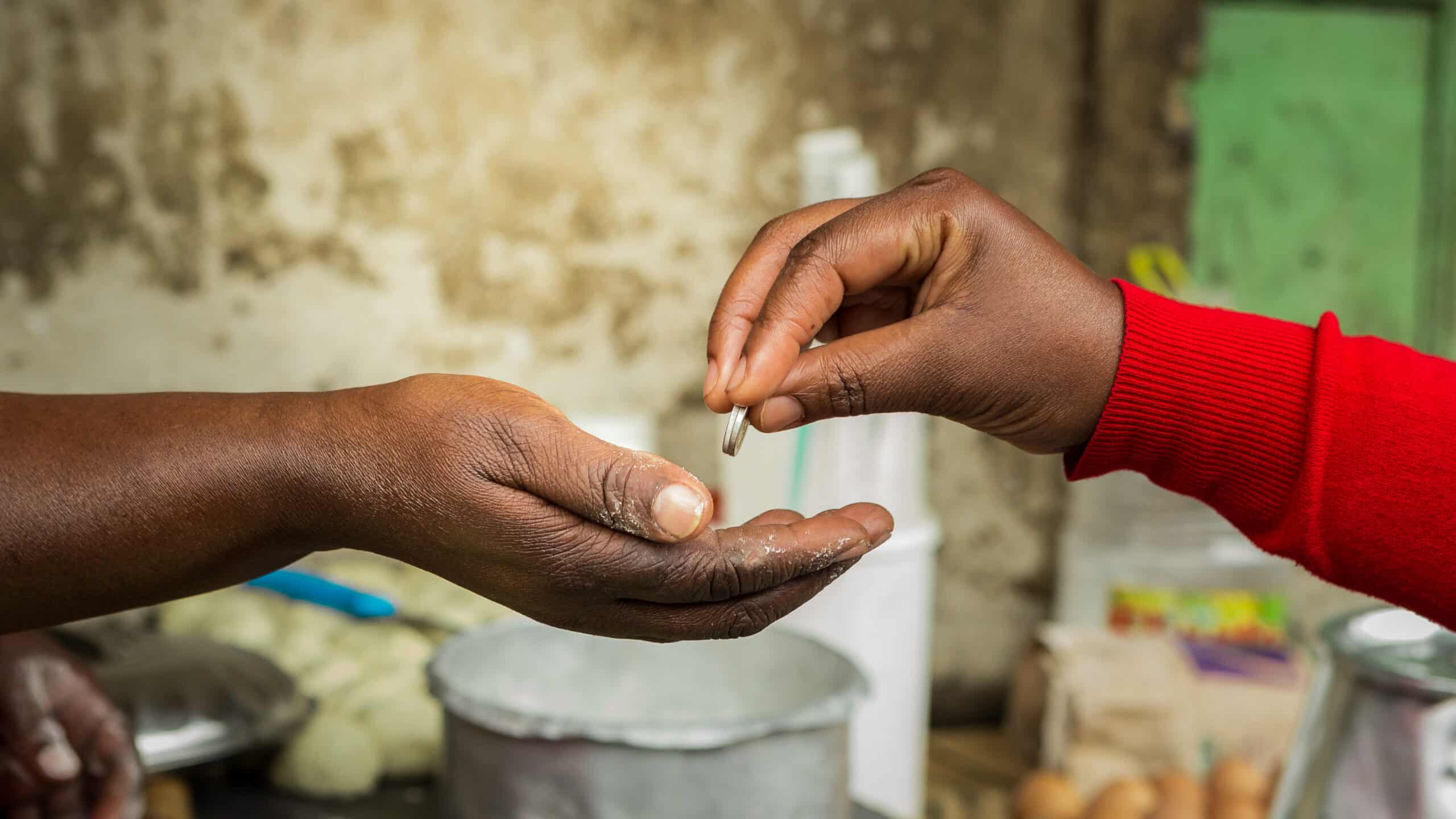
However, low-income women often face barriers to accessing a safe place to save due to mobility and time constraints as well as low levels of financial literacy. They are forced to save in less reliable ways: at home in a drawer or under a mattress, by buying excess stock for their businesses or through a neighborhood savings club.
In Nigeria, Women’s World Banking’s research revealed a strong savings culture. Women running businesses in the bustling urban markets of Lagos put aside as much as 60 percent of their daily income in informal savings tools such as ajo, adako and other methods. What was most surprising though—these women’s businesses were located literally steps from bank branches. Why were they not opening savings accounts?
The answer—the distance is emotional, not physical. These market women are familiar with banks yet they do not see them as relevant or accessible. Even those who have accounts usually place most of their money in traditional, though more informal, financial tools. Diamond Bank set out to close this gap by offering an innovative and relevant savings product that crosses the barriers preventing low-income Nigerians from accessing formal financial services.
Planting a Seed: A transformational savings account
The BETA (meaning “good” in pidgin English) account targets self-employed market women and men who want to save frequently (daily or weekly). The account can be opened in less than five minutes and has no minimum balance and few fees.
Because these clients, especially women, value convenience, the product is built around serving women in the market where they work. Agents, known as BETA Friends, visit a client’s business to open accounts and handle transactions, including deposit and withdrawal, using a mobile phone application.
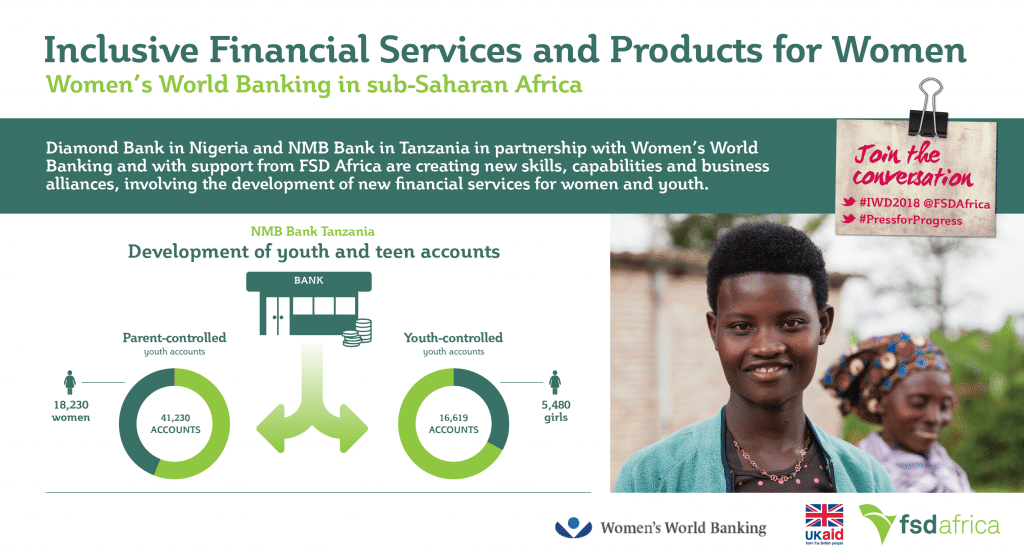
With support from FSD Africa, Women’s World Banking and Diamond Bank are expanding on the BETA proposition to offer women more financial tools and services, including BETA Target Savers, a long-term savings account to help clients work toward larger goals.
Today, Diamond Bank has more than 520,000 new savings account holders who are using these valuable tools, more than 197,000 of whom are women. That’s more than a half million low-income clients who did not previously have access to Diamond Bank, a bank often just steps away from their businesses.
One woman client, who has BETA Friend agents visiting her market stall regularly to collect deposits, put it quite simply:
I want them to be coming around often so that I can save my money, so I can use it to do better things for myself.
With Target Savings, we’re hearing a similar sentiment. A woman client said,
You keep your money to achieve what you want to do. You keep in the back of your mind to achieve your goal.
When we look at how women are able to “press for progress” in their own lives, we know that true financial inclusion is not just about opening accounts, but meaningful usage of these accounts to achieve financial goals and build a better future. Women’s World Banking’s partnership with Diamond Bank is at an exciting phase of the project where we can start to understand just how transformational these savings accounts will be.
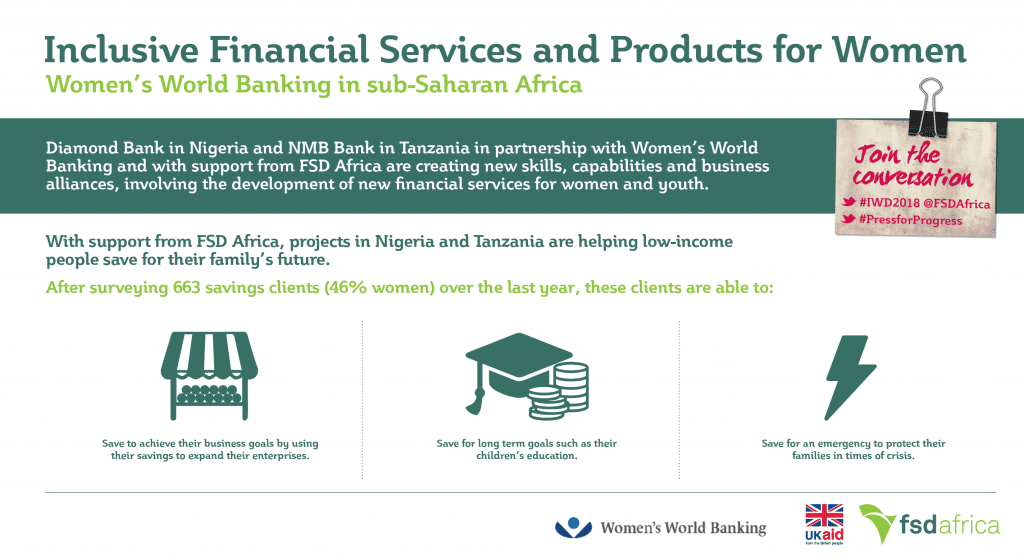
While we’re in the very early stages of analyzing the data, Women’s World Banking is looking at exactly how clients are doing this. After conducting a baseline survey in 2015 as well as a follow up survey in late 2017 to measure how clients are using the savings accounts to improve their lives, we are seeing promising early results, specifically in using savings to grow businesses and achieve goals.
Clients are reporting using their savings to fund business expansion. This is a critical point as financial services for low-income women are often associated with micro loans, and while credit is an important tool, savings is essential for women to grow their businesses.
Additionally, time and time again, when Women’s World Banking asks women about their primary savings goals, education for their children is at the top of the list. Initial survey results are showing that BETA clients are saving for their children’s education and are more likely to have all of their school-aged children in school.
On International Women’s Day, we’re happy to celebrate these promising signs of progress for women in Nigeria. We look forward to continuing to learn more about how savings tools can help women to press for progress.
This blog was published by Women’s World Banking http://www.womensworldbanking.org/news/blog/international-womens-day-women-save-succeed/
















 ,
,