Together with FSD Uganda, we have been supporting the Financial Inclusion for Refugees (FI4R) project where 3 financial service providers (FSPs) have been offering financial products to refugees and host communities in West Nile and South-West regions. The implementing partners – Equity Bank Uganda Limited, VisionFund Uganda, and Rural Finance Initiative – started off activities in these areas in September 2019.
In January 2020, the project engaged BFA Global to undertake a baseline study that provided an in-depth analysis of the incomes, expenses, and financial management of refugees in Uganda, compared their status then, with their lives prior to leaving their countries of origin and their journeys to Uganda. This was followed by four rounds of financial diaries over two years using BFA Global’s financial diaries methodology.
The results from each round are below.
- Financial Inclusion for Refugees (FI4R) – Results of round 1 diaries
- Financial Inclusion for Refugees (FI4R) – Results of round 2 diaries
- Financial Inclusion for Refugees (FI4R) – Results of round 3 diaries
- Financial Inclusion for Refugees (FI4R) – Results of round 4 diaries
The financial diaries involved tracking incomes and spending habits of 41 households recruited from the three implementing partners. During each round, qualitative interviews were also conducted with the households. In November 2021, an end-line study was conducted to understand the evolved financial behaviour of refugees, get feedback on financial products offered by the implementing partners and assess how new financial products were used by the refugees. The Covid-19 pandemic occurred during the study period and offered the opportunity to track how households coped with the situation. Below is a timeline of the research activities undertaken dung the project.

The end-line report dubbed, Rebuilding Livelihoods in Displacement has shown there is increased use of cash at home as refugees seek easy access to money in case of emergencies, despite the growth of phone ownership which supports mobile money transactions. According to the study, refugees found the use of cash convenient in responding to emergencies, especially those that are health-related. The study which sought to examine the financial strategies employed by refugees attributed increased phone ownership to the 2019 legislative changes which allowed refugees to access SIM cards in their names. Ownership of smartphones is 9% higher among female refugees compared to men.
The report further revealed that while refugees have a wide range of income sources, self-employment remains one of the primary sources of income. However, proceeds from agriculture are on the rise with more people paying attention to the sector because of reduced food rations. The report found access to banking agents to be low which limited the use of formal financial services. Most agents are found at the centre of the settlements which is far from some of the refugees.
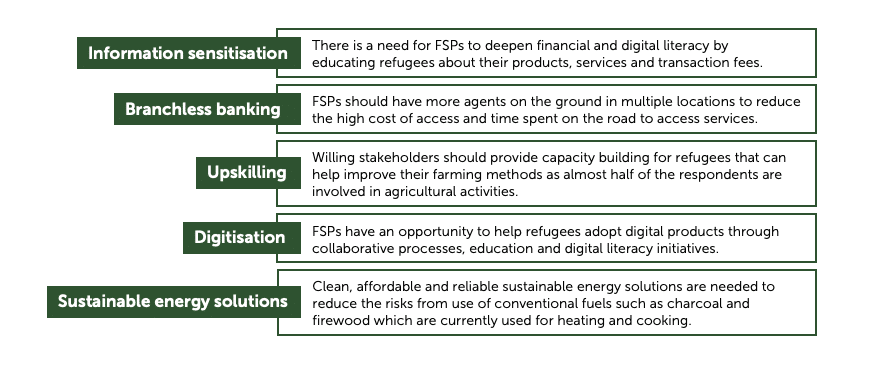
The report recommends the development and refinement of financial products to cater to the needs of refugees. These could include branchless banking to make financial services more accessible and microinsurance for medical emergencies. The report recommends the provision of renewable energy solutions for lighting and cooking and upskilling for economic self-sufficiency.
With about 30 million refugees on the continent, the findings could provide insights for other refugee populations outside of Uganda.