There is much talk lately about blended finance, the use of capital from public or philanthropic sources to increase private sector investment for sustainable development. I was on a panel earlier this year when one of the speakers described it as ‘the trampoline that can give you the bounce needed to launch.’
Smart deployment of blended finance not only provides early capital to sustainable solution but can guarantee long-term financing by attracting private and institutional investors.
FSD Africa Investment’s form of blended finance, development capital, is designed to invest in untested, breakthrough ideas that we believe can have a transformative impact on the continent’s sustainable growth. Our investment works to take early stage risk, allowing other sources of risk capital to invest in high-impact financial sector intermediaries and business, alongside us. Why is this important?
Africa needs investment capital with different risk/return profiles
Reaching the S require private and institutional capital to invest in structures that achieve development outcomes in a financially sustainable way.
We invest in high-potential businesses that are often deemed too risky for commercial investment. The ‘trampoline effect’ makes it easier for commercial capital to flow to ventures that now match their risk/return profiles. For example, our investment in <a”https://fsdafrica.org/programme/mfs-africa/”>MFS Africa, a remittance payments provider, enabled them to close their Series B round, and grow to raise capital in future funding rounds.
African SMEs need early stage risk capital
For investors seeking returns, Africa is a continent of opportunity, but also high risk. Medium and SMEs account for 90%1 of Africa’s businesses and contribute to 40% of GDP, as well as creating 80% of the continent’s employment. The reality, however, is that the majority of African SMEs are in the early stages of their development, with investment needs between USD 50,000 and USD 500,000, but struggling to access capital to expand and grow into larger and more sustainable companies as they are deemed to high risk.
Our mandate is to change this perception, by testing new and alternative financing structures that can make investing in Africa’s SMEs more attractive to investors.
Africa needs investments in businesses that will increase access to basic services
The majority of people in Afrnot have access to affordable health services, opportunities to save for old age, safe water and clean energy or housing. With a projected population of 2.4 billion by 2050, the need has already surpassed the ability of governments and development finance institutions to address this crisis.
FSD Africa Investments development capital is critical to engaging the private sector, as well as institutional and impact investors, to fund businesses and products that can expand access to basic services for everyone. For example, we are already investing in an affordable housing finance company and a micro-pensions start-up.
Africa needs more private sector solutions for climate change
Millions of vulnerable people are falling into poverty as a direct consequence of climate change. Extreme climate conditions are affecting livelihoods – with loss of property, income, access to clean water and a safe environment. Trillions of dollars of investment are needed to combat climate change. We need to move quickly towards renewables, sustainable agriculture and energy efficiency.
We deploy development capital to mobilize financial resources into financial platforms and solutions to mitigate the causes of climate change and to adapt to its effects, reducing its impact.
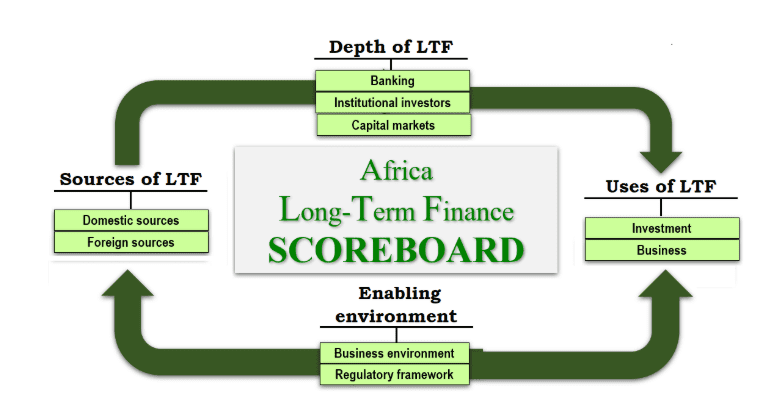
Africa’s needs to harness its own sources of capital
Foreign Direct Investments to Africa have been on a downward trend over the last five years, falling from USD 74 billion in 2013 to 42 billion in 2017. Yet, Africa has large pools of its own capital through savings, insurance, pensions contributions but very little of thisoney finds its way back to the real sector or into alternative asset classes, such as private equity funds. Finding investment platforms that use blended finance structures to manage the risk/return profiles would support a better allocation of this capital to the real economy.
Unlike many development finance institutions, we have a primary mandate to drive impact, which is secondary to the need to create return on our investments. We invest in order to drive impact and create solutions to the most pressing challenges facing Africa’s financial markets.
By stimulating and increasing the flow of commercial and institutional capital into financial firms and funds, we’re ensuring that Africa’s financial sector can serve its local communities and economies in the long-term, reducing the need for development funding in the future.
<cite”blockquote-source”>1The Challenges and Opportunities of SME financing in Africa, London Stock Exchange Group,